THC, Tetrahydrocannabinol, is a highly psychoactive cannabinoid that is naturally present in hemp and cannabis. It is among the main cannabinoids that are responsible for the “high“. THC directly interacts with the human endocannabinoid system and influences the way people think, feel and perceive things.
Beyond its recreational reputation, many studies have revealed that THC can be very beneficial for some medical conditions, like relieving pain, reducing nausea, and supporting mental relaxation.
The History of THC Discovery
Cannabis has been cultivated for thousands of years in ancient China. Hemp served multiple purposes, from healing remedies to textile production. Over time, hemp cultivation spread to Europe and later to America.
In the 1600s, many hemp plants started to grow in American colonies for making cloths, ropes and fabrics. In some regions, hemp was even accepted as legal tender. During the 20th century, especially in the 1930s and 1940s, cannabis began to be used rapidly for recreational purposes.
In 1964, Israeli chemist Dr Raphael Mechoulam and his team made a groundbreaking discovery. They identified THC — the main psychoactive compound in cannabinoids. They successfully isolated it from hemp plants through various extraction methods. Since then, researchers have continued to explore THC effects, chemical nature, and medical values.
How Does THC Work?
When you inhale THC, through vaping or smoking, it enters the endocannabinoid system (ECS) and is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream. It strongly binds with endocannabinoid receptors in the brain and nervous system, which triggers a series of chemical reactions.
These interactions activate neurons that are responsible for concentration, coordination, pain perception, cognition, and time awareness. As a result, it provides calming, relaxing, and deep euphoric effects.
In simple words, THC temporarily influences or modulates the body’s natural system, enhancing feelings and sensations. It makes THC more valuable for both fascinating effects and therapeutic potential.
Types of THC
Medicinal Health Benefits of THC
THC has been used for centuries for natural healing remedies. Many modern scientific studies also suggest that THC offers several therapeutic benefits while giving psychoactive effects.
1. Pain Relief (Analgesic Effects)
THC strongly binds with endocannabinoid receptors in the brain, helping to reduce pain perception.
Modern research “A Rapid Systematic Review of Randomized Control Trials” shows cannabinoids like THC help relieve neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia.
“Journal of Cannabis Research” also found its potential therapeutic effects. Medicines containing THC help to improve sleep quality and comfort in chronic pain patients.
2. Reducing Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting
THC directly interacts with the body’s natural system. It makes THC useful for combat chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV).
“PubMed – Antiemetic Efficacy of THC/CBD” trials show that THC and CBD cannabinoids help in managing nausea after chemotherapy.
“Springer – Cannabis in Chemotherapy” and” Cochrane – Cannabis-Based Medicine Review” also support that THC is beneficial in managing CINV.
3. Appetite Stimulation and Weight Support
THC can help to improve food intake and weight gain in chronically ill patients. “American Cancer Society – Benefits of Cannabis” also highlights these therapeutic effects during cancer treatment.
4. Sleep and Relaxation
THC often provide deep relaxation by reducing excessive neural activity in the brain. “ScienceDirect – THC and Sleep Study” found that a low dose of THC improves sleeping patterns.
5. Mental Relaxation and Mood Regulation
THC influences neural activity by stimulating dopamine and serotonin pathways. The brain goes into a calming state and helps to reduce anxiety, stress, and fatigue.
“MDPI – Cannabinoids and Mood Research” suggests that a small dose of THC helps in emotional regulation.
6. Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Potential
THC directly enters in endocannabinoid system and binds with CB1 and CB2 receptors in the brain. “THC Overview” shows that it protects brain cells and reduces inflammation or oxidative stress.
Side Effects of THC
THC has several therapeutic benefits, but if used improperly can cause temporary side effects. It must be consumed in moderation and responsibly.
- Dry mouth
- Red eyes
- Dizziness
- Mild anxiety
- Nausea
- Increased heart rate
- Short-term memory issue
- Sleepiness
Potential Health Risks of THC
THC is a highly psychoactive cannabinoid. When consumed in high doses or without any proper guidance, it can cause serious health issues over time.
- Regular usage can build tolerance and reduce euphoric effects.
- Long-term use of THC can cause psychosis, particularly among adolescents and adults.
- Excessive use can lead to impaired coordination & reduced focus.
- High doses can affect the heart rate and lung tissues.
- Long-term THC usage can cause neurotoxic effects and change brain structures.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding mothers should avoid THC, as it can worsen anxiety disorders.
- THC causes compensatory mechanisms in the brain, reduced gray matter in the prefrontal cortex and increased neural fiber density.
Safety Tips for Responsible Use
To enjoy THC euphoric effects and ensure safety, you must follow these best practices
- Start with a small dose and then gradually increase.
- Don’t mix it with any sedatives or alcohol.
- Stay hydrated to avoid dryness and dizziness
- Always use lab-tested products.
Safety Tips for Responsible Use
THC can be consumed in several different ways. It depends on personal preference and desired results.
Smoking: Dried cannabis flowers are ground and rolled into a joint or used in a pipe for quick and strong effects.
Vaping: Use dry herbs and concentrates in vapes and enjoy their smooth flavor. Vaping gently heats them without burning.
Homemade Edibles: THC can be added to your favorite recipes in form of gummies and exotic dry flowers.
Tinctures: THC tinctures are usually taken under the tongue for controlled and fast relief.
Capsules: THC capsules are pre-measured doses and ideal for consistent or discreet use.
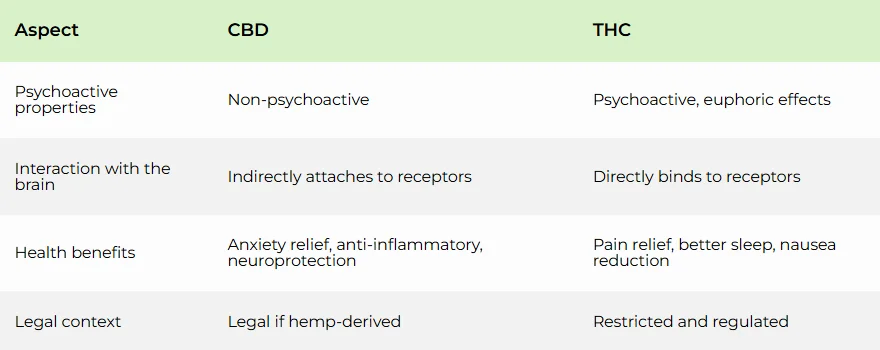
THC vs CBD – Key Differences
THC and CBD are both cannabinoids that are naturally found in cannabis plants. Their origin is the same, but their effects on the body and brain are different.
Psychoactive properties
THC is a psychoactive compound and delivers euphoric, energizing effects. In contrast, CBD is non-psychoactive and does not cause any high or intoxication.
Interaction with the brain
THC directly binds with endocannabinoid receptors, while CBD indirectly attach with brain receptors. CBD helps to balance the psychoactive effects of THC, supporting homeostasis.
Health benefits
THC helps relieve pain, reduce nausea, and improve sleep. On the other hand, CBD is best for anxiety relief, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotection, and seizure reduction.
Legal context
CBD is legal in many countries if derived from hemp plants that contain less than delta-9-THC. However, THC remains restricted and regulated. Always check your local laws before use.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does THC stand for?
THC stands for Tetrahydrocannabinol. A psychoactive compound that is naturally present in hemp and cannabis plants.
How long do the effects of THC last in the body?
The exact duration of THC lasting depends on the body chemistry, consumption methods. Vaping and smoking give instant results but fade faster. In contrast, THC edibles take some hours to show their results but last for several hours.
Can THC be used medicinally?
Yes, THC has proven medicinal benefits that are supported by many research studies. It helps to reduce nausea, relief pain, improve appetite and promote better sleep.
Is THC Legal?
THC laws vary from country to country. Some countries permit their recreational and medical usage under strict regulation. It’s restricted in many regions because of its psychoactive nature.